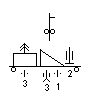Updated by |
On 10/10/2017 |
Basic Organization of Schützen-Regiment (mot.) in 1939
| Created by |
| Dr.Chuang |
| on 18/1/1998 |
For more information about Panzergrenadier, please visit our entrance site as below. |
Reorganization of Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1, 2, and 3. The first three regiments were also reorganized during 1935 to 1939, mainly to increase their firepower (Table 7, Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 as an example). The regiment HQ had one motorized signal platoon and two battalions. Each battalion contained five companies. There were one motocycle rifle company, two motorized rifle companies, one motorized heavy machine gun company and one motorized heavy rifle company in each battalion. But their equipment and organization were quite different from that in 1935 (Table 2).
Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 in 1939
 1. 1. |
|
|
|
|
Table 7. Basic organization of Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 in 1939. The battalion and company levels show the traditional German tactical symbols.
The firepower of both motorized and motorcycle rifle companies were increased by heavy machine guns and light mortars. In addition to heavy machine guns the motorized machine gun company also had heavy mortars. The motorized engineer and anti-tank gun platoons were still remained in the motorized heavy rifle company, but the motorized light mortar platoon was replaced by the more powerful motorized light infantry gun section. The overall firepower of these regiments in 1939 (Table 8, Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 as an example) was increased as compared to that in 1935 (Table 3).
Firepower of Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 in 1939
|
light/heavy MG |
5 cm/8 cm Mortar |
3.7 cm Pak |
7.5 cm light IG |
|
| Stab | ||||
| I. Bataillon | 31/14 | 9/6 | 3 | 2 |
| II. Bataillon | 31/14 | 9/6 | 3 | 2 |
| Total | 62/28 | 18/12 | 6 | 4 |
Table 8. Firepower distribution in Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 in 1939, MG: machine gun, IG: infantry gun.
Creation of 10. Panzer-Division. 28 March 1939, Prague, 10. Panzer-Division was created as an occupational force of Czechoslovakia. The units under its command were exchanged from other mechanized formations. The major combat components that assigned to the division were Panzer--Regiment 8 from 4. Panzer-Brigade, Infanterie-Regiment (mot.) 86 and II. Abteilung/Artillerie-Regiment (mot.) 29 from 29. Infaterie-Division (mot.), and I. Abteilung/Aufklaerung-Regiment 8 from 3. leichte Division.
Creation of the Panzerverband Kempf. 10 August 1939, East Prussia, Panzerverband Kempf was activated for the autumn maneovurs. The divisional group was an ad-hoc brigade-sized unit and was named after its commander, Generalmajor Werner Kempf. The major combat components that assigned to the divisional group were Panzer-Regiment 7, SS-Standarte Deutschland (mot.) and SS-Artillery-Regiment (mot.). The divisional group was amalgamated into 10. Panzer-Division after the Polish Campaign was over. The Waffen-SS units were returned to SS-Verfügungs-Division.
Formation of gepanzert Schützen-Kompanien in Panzer-Division. Since the foundation of panzer divisions long before the outbreak of World War II and during Polish campaign, most of the German motorized rifle units had to reply on lorried borne vehicles due to lack of suitable armor transport vehicles. Thus motorized riflemen had to fight dismounted and could not always follow the panzers into action, some quick successes gained by the panzers could not be fully exploited due to lack of riflemen support especially in street fighting, night actions and in difficult terrains. It was necessary to equip motorized rifle units with a new vehicles not only for transportation both on road and cross-country to follow the panzers, but also provided armor protection for riflemen riding on the vehicles. This concept led to the introduction of an armor halftracked fighting vehicle, the mittlere gepanzert Mannschafttransportwagen (MTW) SdKfz 251. The first 68 MTW were delivered to 1. Panzer-Division in three armored rifle companies in Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 during Polish Campaign.
List of Composition in Schützen-Regiment (mot.) in 1939. There were eight motorized rifle regiments in seven panzer divisions.
| Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 1 | 1. Panzer-Division |
| Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 2 | 2. Panzer-Division |
| Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 3 | 3. Panzer-Division |
| Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 12 | 4. Panzer-Division |
| Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 13 | 5. Panzer-Division |
| Schützen-Regiment (mot.) 14 | |
| Infanterie-Regiment (mot.) 86 | 10. Panzer-Division |
| SS-Standarte Deutschland (mot.) | Panzerverband Kempf |
There were total 79 motorized rifle-related companies in eight motorized rifle regiments and the composition included 41 motorized rifle companies (52%), 12 motorized MG companies (15%), 12 motorized heavy companies (15%), 11 motorcycle rifle companies (14%), and 3 armored rifle companies (4%).
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Member of |
| Associated with |

 II.
II.